ERP vs. CRM: What are the Differences?
For every successful organization, there comes a point when you must choose a technical solution to help you organize and analyze the company's data and processes. You can no longer do all your business via spreadsheets and notes.
At first glance, both CRM and ERP systems aim to improve the productivity of the business by simplifying data management and automating some operations. However, there are important distinctions between CRM and ERP that you need to understand before purchasing these solutions.
In this article, we compare ERP and CRM systems, go through the similarities and differences between the two, and explain how to determine which solution you need to acquire first. But before that, let's define what ERP and CRM are.
What is ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to a technology that helps companies manage and track their resources and business operations. It serves as a central database for all the activities inside your company. There are three main areas where ERP systems are needed:
- accounting and finances, including the general ledger (GL), accounts payable, accounts receivable, and payroll;
- material requirements planning processes, such as supply chain management, including procurement, inventory management, demand forecasting, and production planning;
- business intelligence, specifically, an overview of the company's internal operations and performance.
Some ERP systems also provide human resources management features such as performance tracking and benefits, however, such features aren't always included in ERP systems.
Here's an example of how an ERP system works. Let's say you want to know how many items you can produce in a week to commit to a bulk order from a new client. Additionally, you want to calculate how many resources (labor, materials, etc.) you'll spend on the production to correctly price the order.
Based on the historical data, an ERP system will quickly calculate the typical production volume and the appropriate pricing. Moreover, if you decide to increase your productivity, you can use an ERP system to find which processes need improvement and utilize business automation features to streamline some routine processes. In this case, you could integrate your ERP software with a CRM solution to automatically generate order pricing every time there's a new potential customer.
All in all, an ERP solution assists in monitoring, organizing, and automating various non-customer-facing processes, particularly those related to production and resource allocation within a company's back-office operations.
Benefits of ERP systems
Improved productivity and performance
Having one center for all the information concerning production and resources helps your employees spend less time requesting information from different departments and decreases the risk of wrong calculations based on outdated data. Moreover, an ERP automates routine tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and accounting. This reduces manual errors and speeds up workflows, leading to increased productivity.
For example, an ERP system can help a company close its financial quarter faster. Finance teams typically account for all income and expenses and calculate the results at the end of each month or quarter. Not only does an ERP system store all the information needed to close the books, but it can also carry out these calculations automatically, only requiring some supervision from the financial department.
Enhanced decision-making
ERP systems offer analytics and reporting tools that provide insights into your business performance. At a glance, you can see how many resources your company requires, how much it produces, and how much profit it makes. This enables the company's leaders to make quick and informed business decisions based on actual data.
For instance, an ERP system can help a company track its spending on different resources and suggest ways to optimize spending, e.g., by finding more affordable suppliers or automating some labor-intensive activities
Aligning production with sales
An ERP system helps align production with demand and makes it easy for various departments to access this information in real-time.
Such features as demand forecasting and resource planning rely on historical data and seasonal trends to safeguard your company from over or underproducing.
Additionally, sales representatives benefit from insights into outstanding payments, credit status, supply chain alerts, and order processing issues available in ERP software. Leveraging ERP tools, they can proactively address potential delays, offer alternatives, and make informed decisions about upselling to customers.
Better resource allocation
ERP systems optimize resource allocation by aligning production levels with demand and analyzing a company's performance, making it easy to see where resources are needed. This leads to reduced waste and improved utilization of resources.
Securing company data
By employing security tools and enabling role-based access to sensitive information, ERP systems safeguard companies from hacking and data leaks. They restrict unauthorized access, encrypt data in storage, track user activities for accountability, and provide ongoing protection against cyber threats through software updates.
What is a CRM?
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management and describes the process of tracking, organizing, automating, and analyzing a company's interactions with its customers via designated software. Such CRM software is typically used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
Here's an example of how CRMs are used. Imagine you're a sales manager at a software company. One day, you receive an automated notification from the CRM that a potential client downloaded a product brochure from your website and filled out a contact form expressing interest in your software. Based on this action and the information in the contact form, the CRM determined that the prospect was ready to buy and assigned it to you.
Using the CRM, you quickly access the lead's profile, where you see their information and the previous history of interactions with your company. Armed with this info, you can reach out to the lead, addressing their specific interests and needs based on the customer data. The CRM can also recommend the next best actions and selling materials based on the best sales practices and previous successful deals.
CRM systems streamline customer interactions, ultimately improving your productivity and strengthening customer relationships.
Read our article about CRM, to get a detailed overview of the topic.
Benefits of Customer Relationship Management
Improved customer relationships
CRM systems help businesses build stronger relationships with customers by storing and organizing customer information, interactions, and preferences. This leads to personalized communication and tailored experiences.
Increased revenue
Customer relationship management software enables sales teams to track leads, manage opportunities, and streamline the sales process. This results in more efficient sales cycles, better lead conversion rates, and increased revenue.
Boost in productivity
CRM systems automate routine tasks, workflows, and processes, reducing manual workloads, eliminating redundancies, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Data-driven decision making
CRM systems offer analytics and reporting tools that provide valuable insights into customer trends, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making and strategy refinement.
Read our article on CRM Benefits, to get a detailed overview of the topic.
Now that the essential functionalities of ERP and CRM are clear, let's look at the core differences between them, and how they affect your choice of software.
ERP vs. CRM: What is the Difference?
| The differences between ERP and CRM software | ||
ERP | CRM | |
| Operations | Back office: finance, supply chain management, project management, and HR | Front-office: sales, marketing, and customer service
|
| Users | Finance and accounting personnels, operations managers, HR managers, and upper-management and executives. | Sales managers and representatives, marketers, and customer service agents. |
| Data stored and analyzed | Internal data pertaining to resources i.e. financial data, production volume, etc. | Leads and customer data meant to create a complete view of their preferences, needs and interactions, and purchase history. |
| Main features | Central database, system integrations, business task automation, accounting, financial management. | Pipeline management, sales forecasting, marketing campaign automation, customer 360-degree view, contact center. |
| Automation | Companies can use ERP automations, such as automatic report generation and invoicing, to improve efficiency in routine internal tasks. | CRM automations, such as automatic lead scoring and case routing, help users manage the customer journey more effectively. |
| Reporting and analytics | ERP systems mainly offer reports dedicated to resource planning, demand forecasting, and performance assessment. | CRM reporting offers insights into customer behavior and sales, customer service, and marketing campaign performance. |
Ultimately, the main difference between ERP and CRM is that an ERP system is a solution to track and automate overall organizational management, including order processing and fulfillment, invoicing, and payroll, while a CRM system is designed to aid customer engagement. In this way, you could say that CRM software helps facilitate activities that generate revenue while ERP software helps track and distribute that revenue.
In most cases, as your business grows, you'll need both tools to organize business data, increase productivity, and boost profit. CRM and ERP are indispensable parts of an effective business IT system, and they are not interchangeable.
However, right now you might find yourself in a situation where you need to implement business automation, but don't have resources to purchase both tools and are not sure which one of them will have a higher impact on growth. This next section will provide guidance on choosing between ERP or CRM software and highlight the important qualities of both options.
Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
CRM and ERP are two options for companies looking to simplify and improve their business processes. Deciding which one you need right now comes down to the primary goals of your company.
If your goal is
- to have a comprehensive understanding of your company's productivity, resource allocation, and financial performance;
- to improve communication and collaboration between manufacturing, financial and other departments;
- to automate routine but time-consuming financial tasks such as invoicing or payroll;
then an ERP solution is a perfect choice.
However, if you aim to build a better customer journey, bring in more leads into your sales pipeline, and increase customer retention, you need a CRM system.
Whether you choose an ERP or a CRM system now, it should align with three key requirements to meet your business needs: integration, customization, and scalability.
- Integration. Eventually, your ERP and CRM software need to integrate with each other to help your company run smoothly. For example, the configure, price, quote (CPQ) process heavily relies on the tight integration of CRM and ERP systems, as CPQ tools need data from both systems and are crucial for numerous businesses. They must also integrate with other business tools like email services and data analysis solutions. For instance, an ERP linked with a CRM system can automatically notify a customer via email about a shipment delay.
- Customization. Both systems need to adapt to your business needs, so they need to be customizable. Customizable CRMs and ERPs should offer you the ability to design new data models and workflow automation sequences.
- Scalability. A scalable solution ensures that as your company grows, the systems you are using have enough power to accommodate it. When choosing ERP or CRM software, make sure they are easily scalable and there's no significant jump in price between different versions of the tool.
With these qualities in mind, selecting a business automation system should be easy. Creatio stands out as a CRM platform that offers easy customization, integration, and scalability thanks to its unique composable architecture.
CRM Creatio includes three distinct products for sales, marketing, and customer service that help you manage customer data and automate workflows. However, Creatio is much more than a CRM – in its base is a powerful no-code platform Studio Creatio that allows users to build their own business tools and automations.
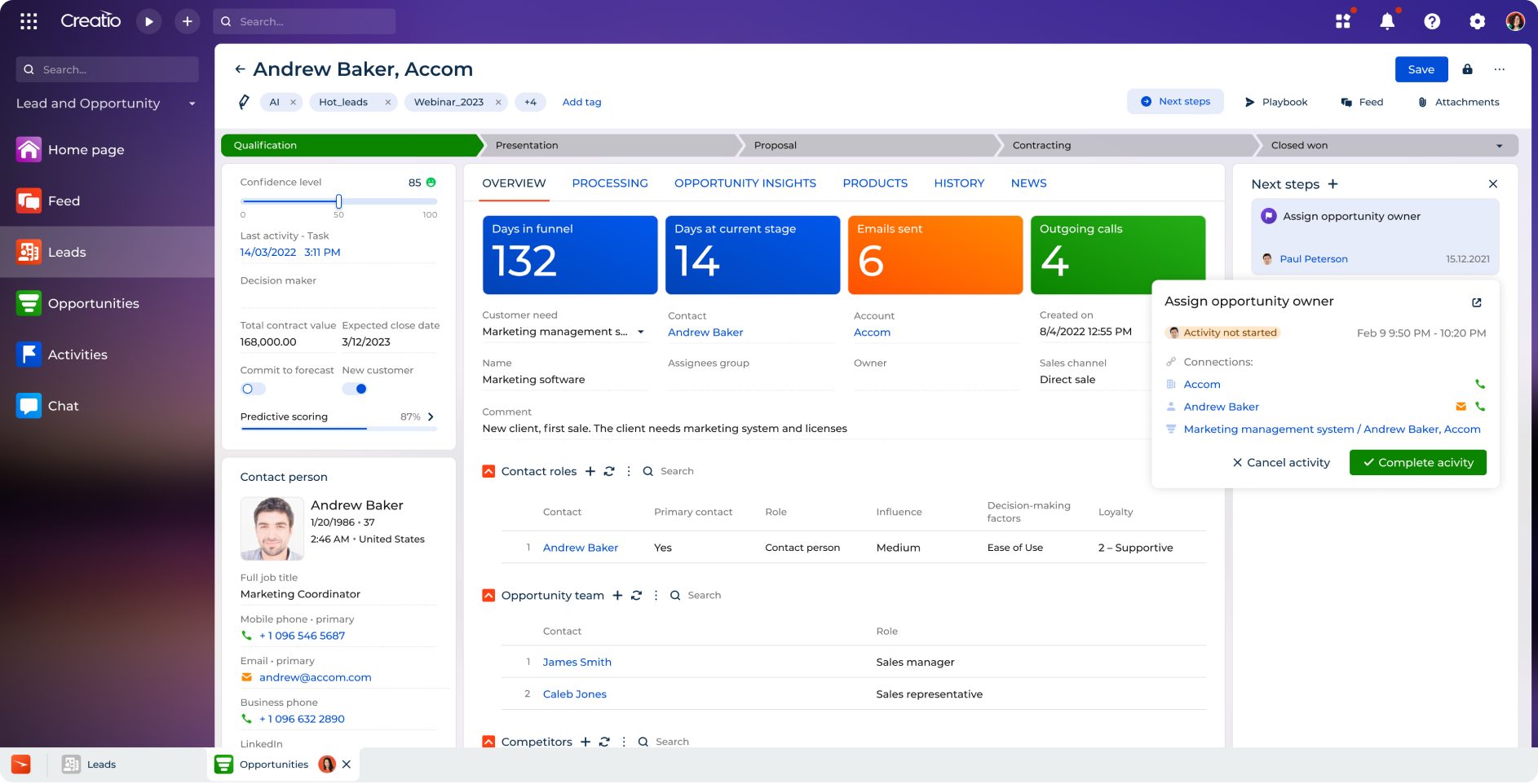
Creatio's 360 customer view
With Creatio's components and drag-and-drop features not only can you build custom automated processes for CRM, but you can also design automations that recreate some ERP functions, which makes it a perfect choice for businesses that don't have the resources to invest in a comprehensive ERP system just yet. For example, Creatio offers prebuild workflow automation for financial management that can help streamline tasks like payroll and invoicing.
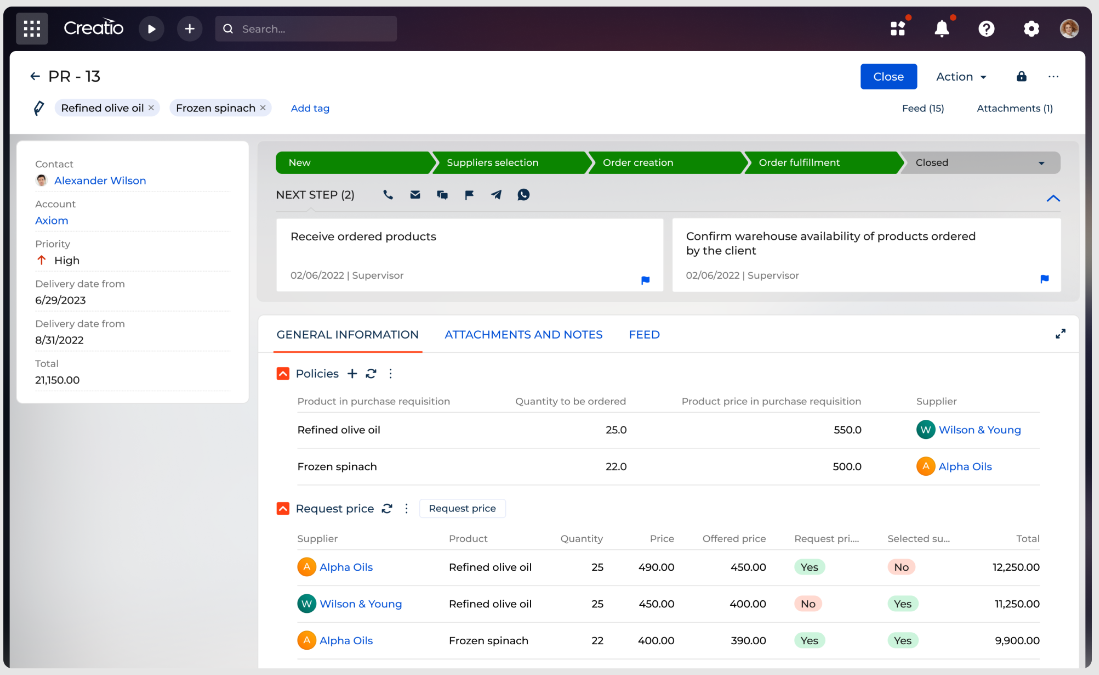
Supply management in Creatio
Creatio boasts a marketplace of more than 700 connectors and applications, including integrations with leading ERP software. Its composable pricing makes it easy to purchase unbundled CRM products and affordably scale your system. You can see Creatio's capabilities for yourself by signing up for a free trial.
Support Your Business with the Right Tools
As you navigate the complexities of choosing between ERP and CRM systems, remember that each solution plays a vital role in enhancing your business operations and achieving your strategic goals.
While ERP systems are essential for managing internal processes, resource allocation, and overall organizational efficiency, CRM systems are indispensable for building strong customer relationships, boosting sales, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Ultimately, the decision between ERP and CRM depends on your business objectives.
Creatio stands out as a versatile CRM platform that offers easy integration with ERP software, customization, and scalability through its unique composable architecture. Explore Creatio's capabilities by signing up for a free trial and discover how it can empower your organization to thrive.

FAQ
Can ERP replace CRM?
While ERP systems can provide some CRM capabilities, they are not a direct replacement for dedicated CRM software, as CRM systems offer specialized tools and features for managing customer relationships and sales activities.
What's the difference between CRM and ERP?
CRM focuses on customer-related activities, while ERP focuses on overall business processes and resource management.
How are ERP and CRM similar?
ERP and CRM systems share similarities in terms of data integration, business process optimization, centralized database management, collaboration support, reporting and analytics, and a focus on improving overall organizational performance.
How much do ERPs and CRMs cost?
CRM software is typically priced between $10 and $90 per user/month depending on the plan you choose. Prices for an ERP system typically start around $180.
Is SAP an ERP or a CRM?
SAP is primarily known as an ERP, but they also offer CRM solutions to help businesses manage their customer interactions and improve customer satisfaction.